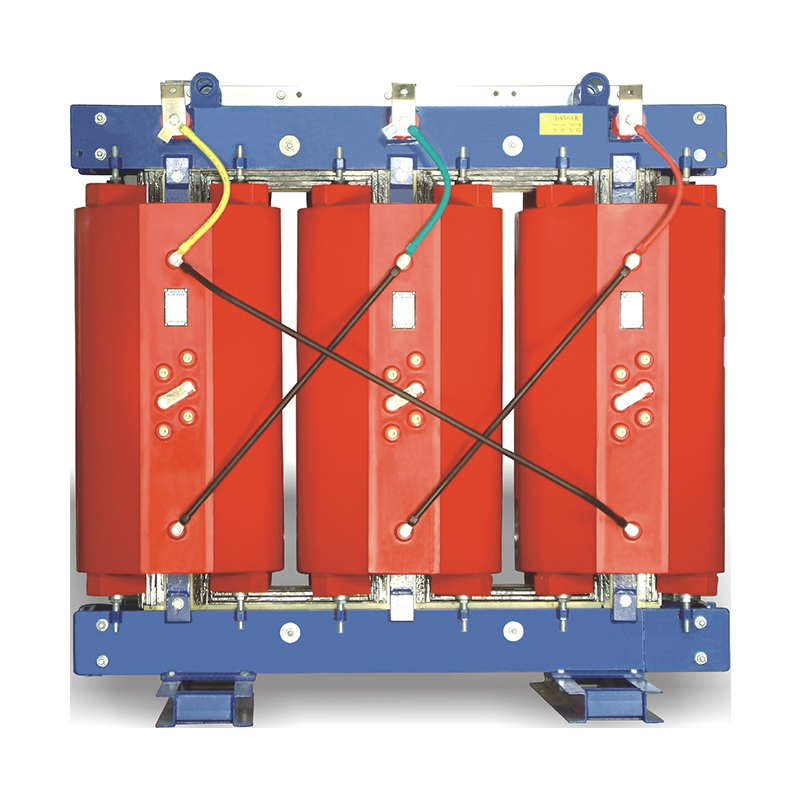
Structure and Process Characteristics of Power Transformer Winding
The structure and process characteristics of power transformer windings are mainly reflected in the following aspects:
1、 Winding structure
1. Winding classification: The windings of power transformers are mainly divided into primary windings and secondary windings. The primary winding, also known as the primary winding, is connected to the power supply; The secondary winding, also known as the secondary winding or secondary winding, is connected to the load.
2. Turn ratio: The turn ratio of the winding determines the voltage ratio of the transformer. By adjusting the turns ratio of the winding, voltage can be increased or decreased to meet different power demands.
3. Winding materials: Winding materials include conductor materials and insulation materials. The commonly used conductor material at present is copper, which has high mechanical strength and good electrical conductivity. Insulation materials are usually made of paper, cardboard, etc. impregnated with liquid insulation materials that can withstand temperatures up to 105 ℃ to ensure insulation performance between turns and layers.
2、 Process characteristics
1. The clamping structure of the winding coil: This is an important part of large power transformers. Reasonably configuring the clamping structure of the winding coil and the clamping parts of the iron core can reduce the electrical stress caused by wire vibration, lightning impulse, and mechanical stress caused by short circuit, thereby protecting the transformer.
2. Cooling method: Power transformers usually use oil immersed cooling method. Transformer oil has good insulation and heat dissipation properties, which can effectively protect the internal components of transformers from external environmental influences. At the same time, the oil tank is also equipped with accessories such as a drain valve, thermometer, and oil level gauge, which facilitate monitoring and maintenance of the transformer.
3. Manufacturing process: The manufacturing process of power transformers includes steps such as winding, dipping, and drying. These steps require strict control of process parameters to ensure the quality and performance of the transformer. For example, during the winding process, it is necessary to ensure that the coil is neat and tight, avoiding problems such as looseness and misalignment; During the immersion and drying process, it is necessary to control the composition, temperature, and time of the paint solution to ensure the uniformity and firmness of the insulation layer.
Overall, the winding structure and process characteristics of power transformers have a significant impact on their performance and service life. In the design and manufacturing process, these factors need to be fully considered to ensure the safe and efficient operation of transformers.
Relatenews
- The Role of Power Transformers in Voltage Regulation within Power Systems 2025-08-25 08:14:00
- Environmental Regulations and Technical Measures for Power Transformer Noise Control 2025-08-25 08:12:00
- The Application of Big Data Analytics in Power Transformer Fault Prediction 2025-08-25 08:11:00
- Impact of Distributed Generation Integration on Load Characteristics of Power Transformers 2025-08-16 09:43:00
- Conditions and Protection Coordination Strategies for Parallel Operation of Power Transformers 2025-08-16 09:42:00
- Application of On-Line Oil Chromatography Monitoring Systems for Power Transformers 2025-08-16 09:38:00
- Capacity Calculation Methods for Power Transformers in Electric Vehicle Charging Stations 2025-08-09 16:02:00
- Key Technologies of Smart Power Transformers: Sensors, IoT, and Big Data 2025-08-09 15:59:00