Detailed explanation of the structural composition of power transformers

The structural composition of power transformers mainly includes the following parts:
1. * * Iron Core * *:
-The iron core is the magnetic circuit part of a transformer, consisting of iron core columns and iron yokes. It is made by stacking silicon steel sheets with good magnetic permeability, usually divided into two types of structures: core and shell.
-There are two types of silicon steel sheets: hot-rolled and cold-rolled. Among them, cold-rolled silicon steel sheets are widely used due to their high magnetic permeability and small unit loss.
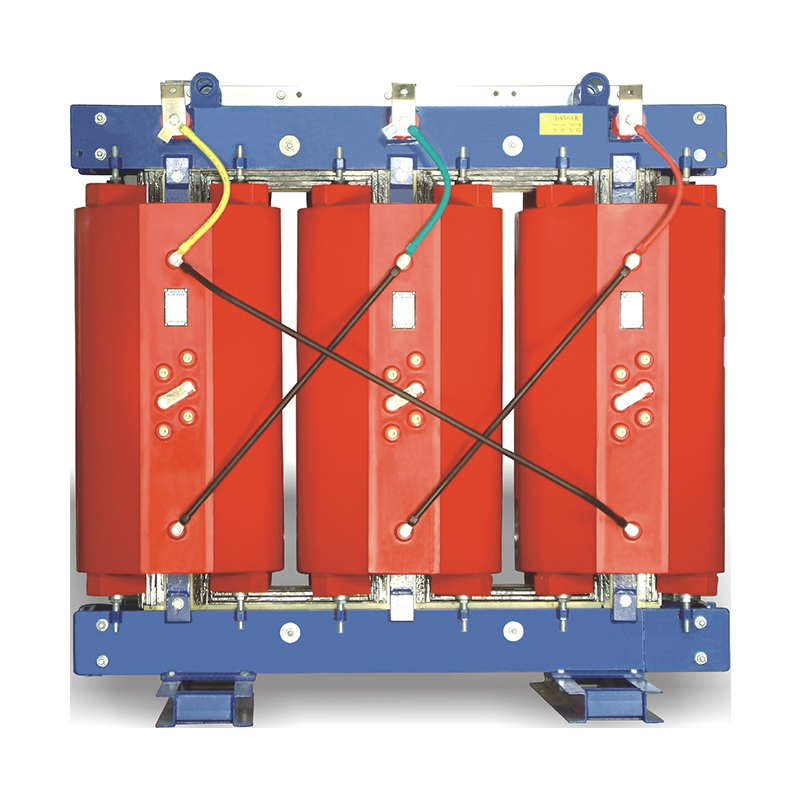
2. * * Winding * *:
-The winding is the circuit part of a transformer, made of insulated enamel, paper wrapped aluminum wire or copper wire. It is wrapped around the iron core and converts voltage and current through electromagnetic induction.
-The winding is divided into concentric and overlapping types according to the different arrangements of high and low voltage. In concentric windings, low-voltage windings are usually placed near the iron core column; In the overlapping winding, the low-voltage winding is placed near the iron yoke.
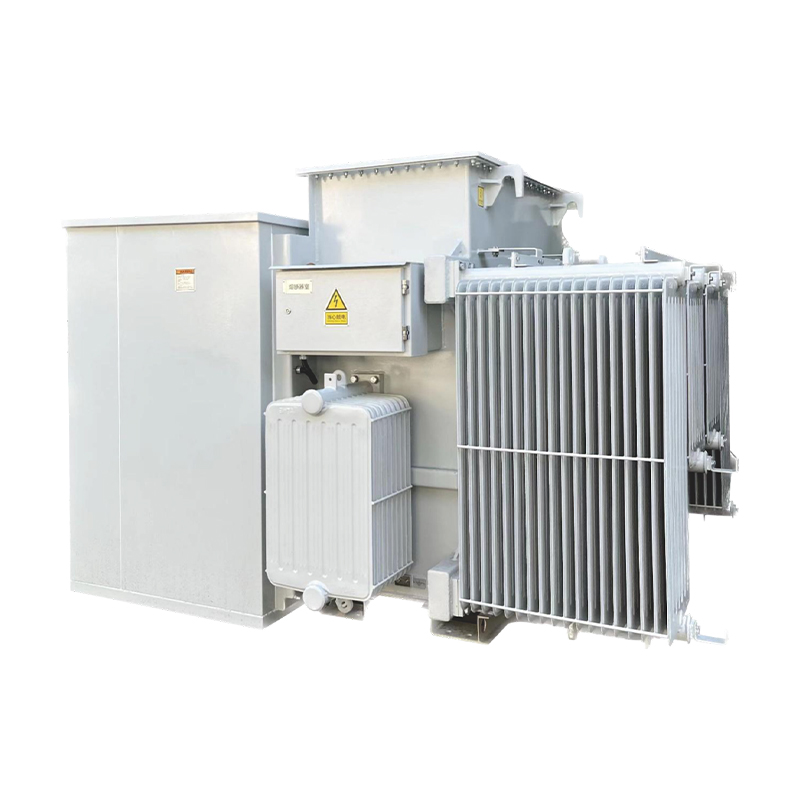
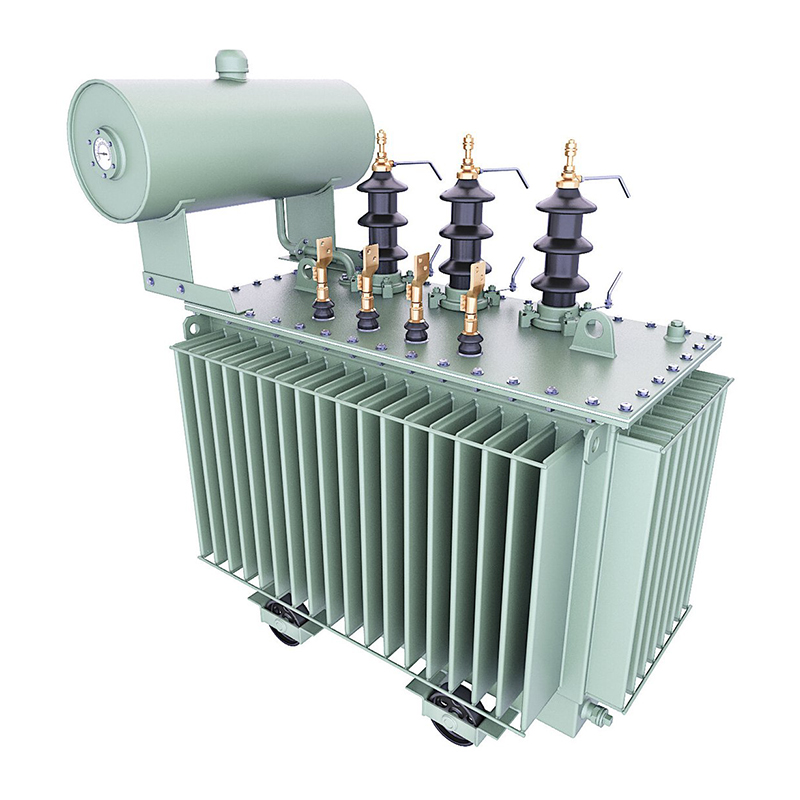
3. * * Fuel tank and accessories * *:
-The oil tank is the outer shell of an oil immersed transformer, filled with transformer oil inside, which plays a role in heat dissipation and insulation. According to different sizes, the fuel tank structure can be divided into two types: suspended body fuel tank and suspended shell fuel tank.
-The accessories include high-voltage bushings, tap changers, low-voltage bushings, gas relays, explosion-proof pipelines, oil pillows, oil level gauges, moisture absorbers, radiators, etc. These accessories play an important protective role in the operation of transformers.
4. * * Insulation material * *:
-The insulation materials inside the transformer mainly include transformer oil, insulation cardboard, cable paper, corrugated paper, etc. These materials ensure electrical isolation between the various components of the transformer, ensuring safe operation.
5. * * Cooling System * *:
-According to the different capacities of transformers, different cooling devices are used, such as natural cooling, forced oil circulation cooling, forced air cooling, etc. The function of the cooling system is to maintain the normal operating temperature of the transformer and prevent equipment damage due to overheating.
In summary, the structural components of power transformers include key parts such as iron core, winding, oil tank and accessories, insulation materials, and cooling system. These parts work together to achieve voltage conversion during the transmission and distribution of electrical energy.
Relatenews
- Detailed explanation of the structural composition of power transformers 2025-01-31 02:52:00
- The Development Trend and Challenges of Intelligent Power Transformers 2025-01-29 02:51:59
- Basic principles and working mechanism of power transformers 2025-01-23 02:51:57
- Sharing of Optimization Ideas for Energy saving and Environmental Protection Design of Power Transformers 2025-01-21 02:51:59
- Design of Oil Tank and Heat Dissipation System for Power Transformers 2025-01-16 09:24:19
- Overload Capacity and Protection Measures of Power Transformers 2024-12-30 09:03:03
- Grounding methods and safety requirements for power transformers 2024-12-30 09:03:02
- Reasons for Noise Generation in Power Transformers and Noise Reduction Technologies 2024-12-30 09:03:01