Design of Oil Tank and Heat Dissipation System for Power Transformers
The design of the oil tank and heat dissipation system for power transformers is a key link in ensuring the safe and efficient operation of transformers. The following is a detailed discussion on these two aspects:
1、 Design of oil tank for power transformer
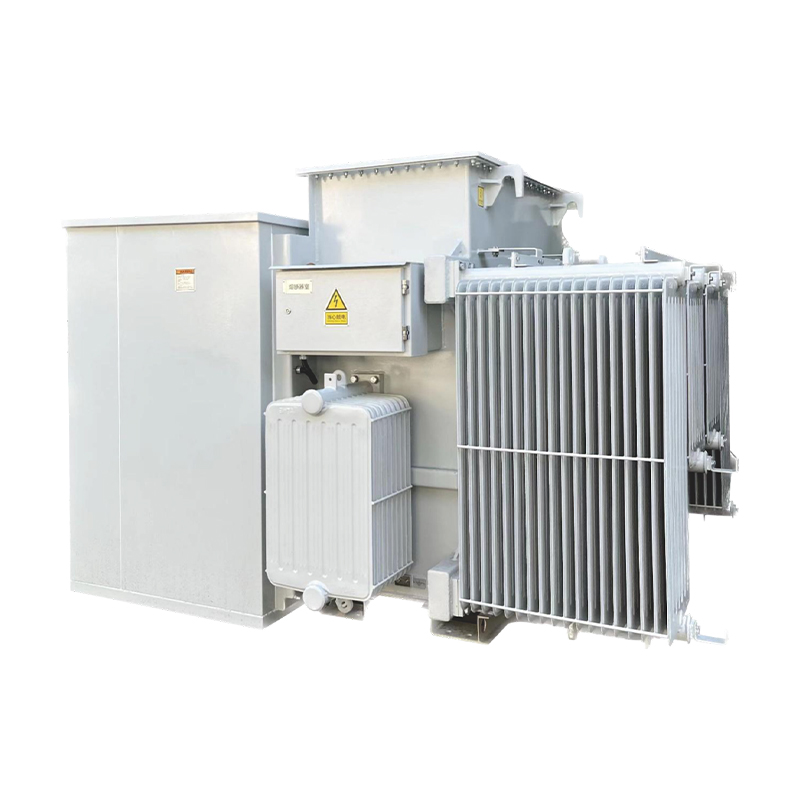
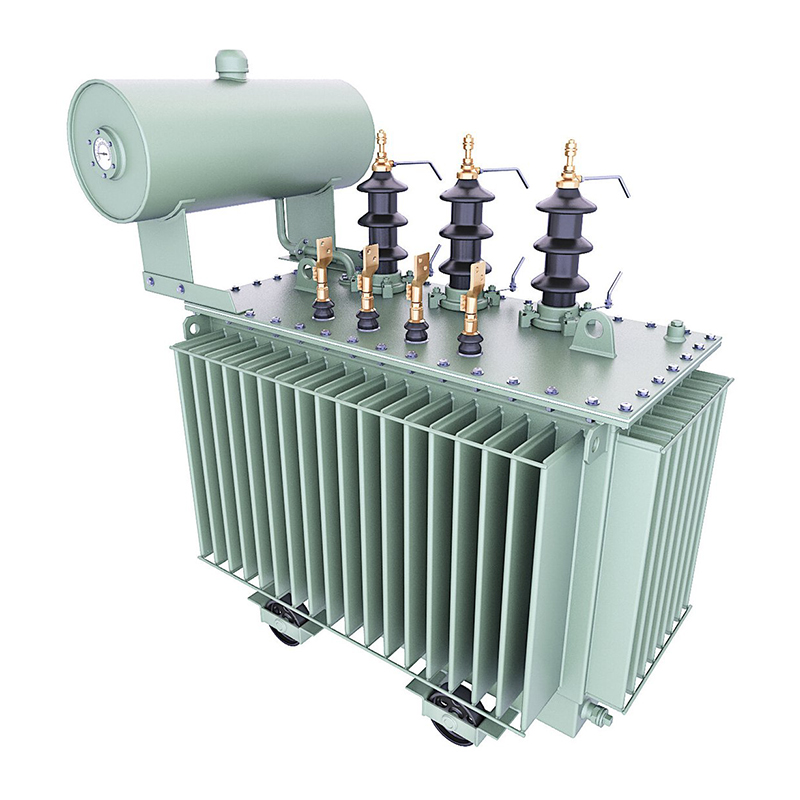
1. Fuel tank structure: As the outer shell of the transformer, the fuel tank not only serves to contain the transformer body and oil, but also plays an important role in heat dissipation and cooling. Therefore, the structural design of the fuel tank should take into account both strength and heat dissipation effect. Generally speaking, the fuel tank adopts a lid type, bell type or sealed structure, depending on the capacity and voltage level of the transformer.
2. Oil tank size calculation: The size of the oil tank needs to be calculated based on the specific parameters of the transformer, including the outer coil diameter, the gap between the high and low voltage sides and the oil tank, etc. Reasonable fuel tank size can ensure the insulation distance and heat dissipation space inside the transformer, thereby improving the safety and reliability of the transformer.
3. Fuel tank material selection: The fuel tank material should have good thermal conductivity, oxidation resistance, and mechanical strength to ensure stable heat dissipation performance and structural strength during long-term operation. Common fuel tank materials include high-quality steel plates and other metal materials.
2、 Design of Heat Dissipation System for Power Transformers
1. Selection of heat dissipation methods: Depending on the capacity and operating environment of the transformer, different heat dissipation methods can be chosen, such as natural cooling, forced air cooling, and heat dissipation with heat sinks. Forced air cooling improves the heat dissipation effect of transformers by installing cooling fans and ventilation systems to force air to cool them. The heat dissipation of heat sink is achieved by increasing the surface area of heat dissipation to improve the heat dissipation efficiency.
2. Selection of heat dissipation materials: Heat dissipation materials should have excellent thermal conductivity and oxidation resistance, in order to quickly conduct the heat generated by the transformer to the outside and reduce the temperature. Common heat dissipation materials include metal materials such as aluminum alloy and copper, as well as non-metallic materials with good thermal conductivity.
3. Temperature monitoring system: In order to monitor and control the temperature of transformers in real time, modern transformers are generally equipped with temperature monitoring systems. The system monitors the temperature changes of transformers in real time by installing temperature sensors and data acquisition devices, and transmits the data to the monitoring center for analysis and processing. Once an abnormal temperature is detected, the system will promptly issue an alarm and take corresponding measures, such as automatically starting the fan to increase heat dissipation or automatically cutting off the load of the transformer, to ensure that the transformer operates within a safe temperature range.
In summary, the design of the oil tank and heat dissipation system for power transformers is a key factor in ensuring the safe and stable operation of transformers. By rational structural design, material selection, heat dissipation method selection, and equipped with effective temperature monitoring systems, the heat dissipation efficiency and safety of transformers can be significantly improved, thereby extending their service life and reducing maintenance costs.
Relatenews
- Basic principles and working mechanism of power transformers 2025-01-23 02:51:57
- Sharing of Optimization Ideas for Energy saving and Environmental Protection Design of Power Transformers 2025-01-21 02:51:59
- Design of Oil Tank and Heat Dissipation System for Power Transformers 2025-01-16 09:24:19
- Overload Capacity and Protection Measures of Power Transformers 2024-12-30 09:03:03
- Grounding methods and safety requirements for power transformers 2024-12-30 09:03:02
- Reasons for Noise Generation in Power Transformers and Noise Reduction Technologies 2024-12-30 09:03:01
- Online monitoring and fault diagnosis technology for power transformers 2024-12-30 09:02:59
- Temperature rise and cooling methods of power transformers 2024-12-26 15:41:20